Crustacean Cardioactive Peptide CCAP
CAS No. 309247-84-5
Crustacean Cardioactive Peptide CCAP( —— )
Catalog No. M30112 CAS No. 309247-84-5
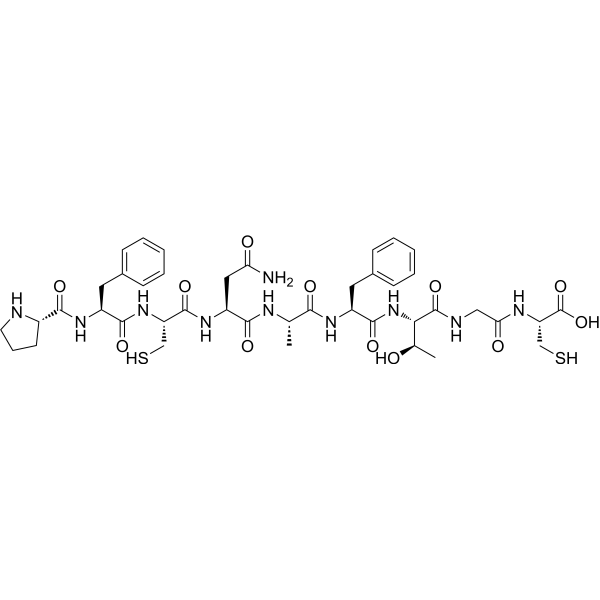
Crustacean cardioactive peptide (CCAP) is a highly conserved, amidated cyclic nonapeptide with the primary structure PFCNAFTGC-NH2 (ProPheCysAsnAlaPheTyrGlyCys-NH2) and a disulfide bridge between Cys3 and Cys9. It is found in crustaceans and insects where it behaves as a cardioaccelerator, neuropeptide transmitter for other areas of the nervous system and a hormone.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 284 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 498 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCrustacean Cardioactive Peptide CCAP
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionCrustacean cardioactive peptide (CCAP) is a highly conserved, amidated cyclic nonapeptide with the primary structure PFCNAFTGC-NH2 (ProPheCysAsnAlaPheTyrGlyCys-NH2) and a disulfide bridge between Cys3 and Cys9. It is found in crustaceans and insects where it behaves as a cardioaccelerator, neuropeptide transmitter for other areas of the nervous system and a hormone.
-
DescriptionCrustacean cardioactive peptide (CCAP) is a highly conserved, amidated cyclic nonapeptide with the primary structure PFCNAFTGC-NH2 (ProPheCysAsnAlaPheTyrGlyCys-NH2) and a disulfide bridge between Cys3 and Cys9. It is found in crustaceans and insects where it behaves as a cardioaccelerator, neuropeptide transmitter for other areas of the nervous system and a hormone.(In Vitro):Ultrabithorax and Abdominal-A are not necessary for specification of the CCAP-interneurons, but are absolutely required to prevent the death by apoptosis of the CCAP-efferent neurons.(In Vivo):CCAP, FMRFamide and SALDKNFMRFamide increase the mosquito antennal accessory pulsatile organ (APO) and heart contraction rates, increase hemolymph flow velocity in the antennal space.
-
In VitroUltrabithorax and Abdominal-A are not necessary for specification of the CCAP-interneurons, but are absolutely required to prevent the death by apoptosis of the CCAP-efferent neurons.
-
In VivoCCAP, FMRFamide and SALDKNFMRFamide increase the mosquito antennal accessory pulsatile organ (APO) and heart contraction rates, increase hemolymph flow velocity in the antennal space.
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number309247-84-5
-
Formula Weight959.1
-
Molecular FormulaC42H58N10O12S2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO : 50 mg/mL (52.13 mM; Need ultrasonic);H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble)
-
SMILES——
-
Chemical NameSequence:Pro-Phe-Cys-Asn-Ala-Phe-Thr-Gly-Cys
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
Suggs JM, et al. CCAP and FMRFamide-like peptides accelerate the contraction rate of the antennal accessory pulsatile organs (auxiliary hearts) of mosquitoes. J Exp Biol. 2016 Aug 1;219(Pt 15):2388-95.
molnova catalog



related products
-
3,8'-Biapigenin
3, 8''-Biapigenin can modulate intracellular ROS production.
-
[pSer2, pSer5, pSer7...
[pSer2, pSer5, pSer7]-CTD (TFA) is a substrate for CDK7(cyclin-dependent protein kinase), a phosphorylated polypeptide at ser2, ser5, and ser7 of RNA polymerase II carboxyl terminus (CTD).
-
7,8,3,4-tetrahydroxy...
7,8,3',4'-tetrahydroxyflavanone is a bioactive chemical.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


